|
|
|
Cotton harvest. Photo: Kimberly Vardeman; Wikimedia Commons. |
Learn how GMO’s are used in bioenergy systems, and why they are controversial in the sustainability debate.
Table of Contents
Current GMO Research
Genetic engineering is being used and tested in virtually every aspect of bioenergy production, including crops, bacteria, yeasts, and catalysts. For example, researchers are trying to genetically engineer plants that grow faster, have high sugar or starch content, contain more cellulose or less lignin, use less water, and have greater resistance to insects and herbicides. Other researchers are trying to genetically engineer biocatalysts—yeasts and other microorganisms that will improve fermentation or facilitate the breakdown of cellulose.
The GMO Controversy
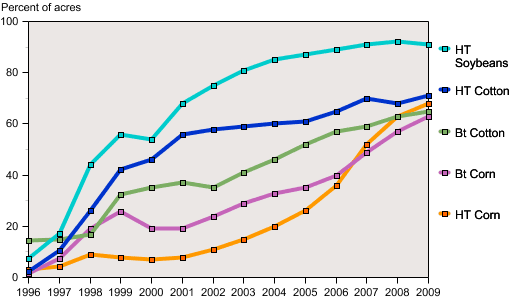
The use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for bioenergy has been controversial among agricultural producers and the general public, especially when these organisms are “transgenic”, containing genes introduced from other species. The use of GMO microorganisms in the manufacturing plant or laboratory, where they are unlikely to interact with the environment, has been far less controversial than the growing of genetically modified crops outdoors. The three major U.S. biofuel crops— corn, soybeans, and canola—are all grown from predominantly transgenic seed.
Concerns about GMOs have included herbicide resistance (the creation of “super weeds”), pesticide resistance, antibiotic resistance, harm to beneficial organisms, loss of biodiversity, and genetic pollution caused by unintended gene transfer. There are also marketing and trade issues (since many countries refuse genetically modified products), liability issues, and a wide variety of food safety issues.
GMOs and Sustainability
The use of GMOs has often been viewed as contrary to sustainability. For example, the Final Rule of the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Organic Program prohibits any use of GMOs in certified organic farming. On the other hand, GMO advocates, developers, and seed companies like Monsanto frequently claim that their products make agriculture more sustainable, not less. While the debate about GMO foods is now decades old, the issues surrounding the use of GMOs in bioenergy systems are only beginning to be discussed.
For Additional Information
Transgenic Crops, ATTRA National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service, 2006.
Contributors
Author
- Mike Morris, National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service (ATTRA)
Peer Reviewers
- Diana Friedman, Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education
- Vern Grubinger, Professor, University of Vermont Extension

