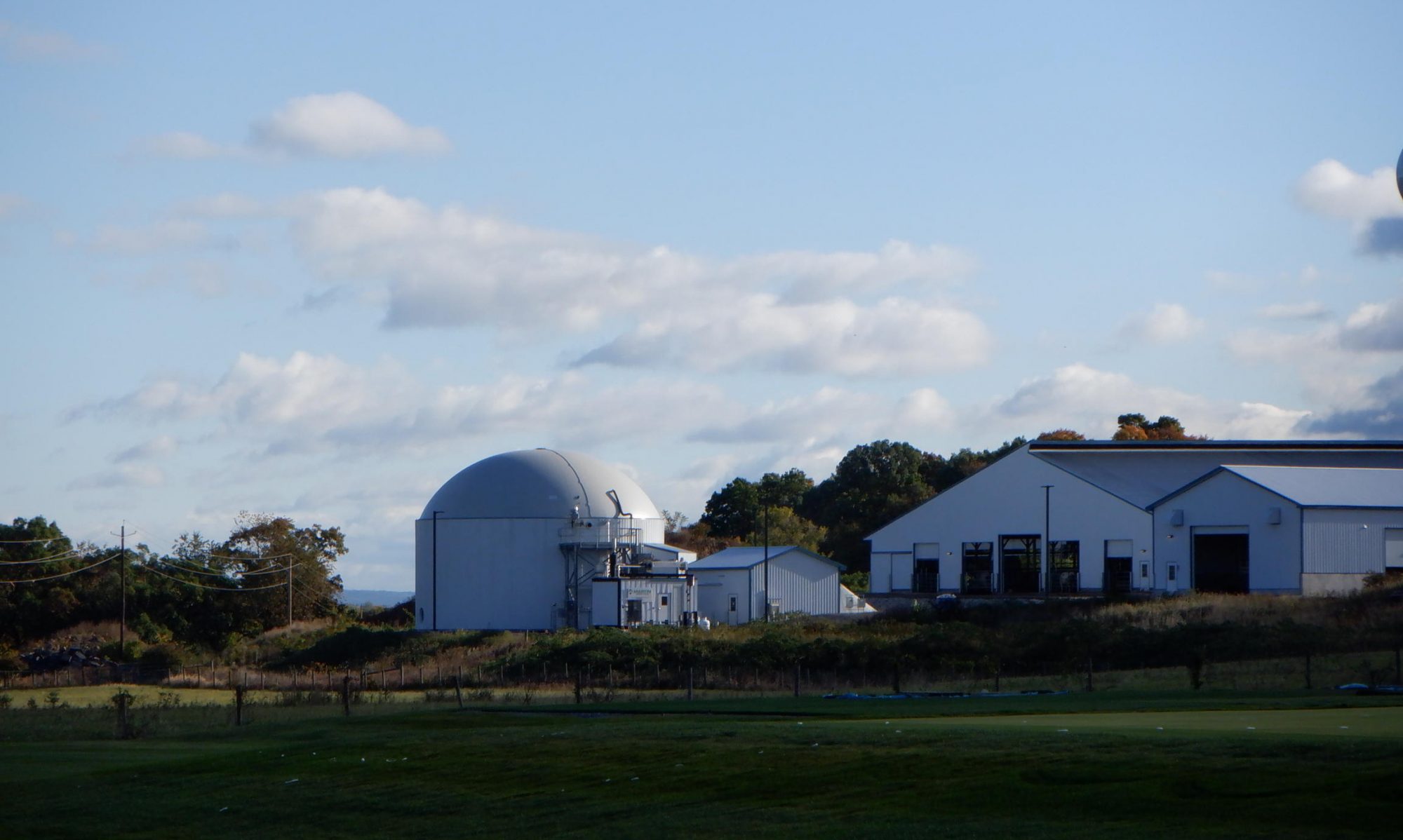
This curriculum module on Greenhouse Energy Efficiency reviews the heat loss calculations needed to determine the (maximum) capacity of a greenhouse heating system. Common greenhouse heating systems are discussed. Natural and mechanical ventilation systems for greenhouses are presented and design parameters provided so that energy consumption by the ventilation system can be determined. Review of several alternative energy sources and systems suitable for greenhouse production. Finally, energy savings strategies are provided along with a calculation tool (Virtual Grower) …





